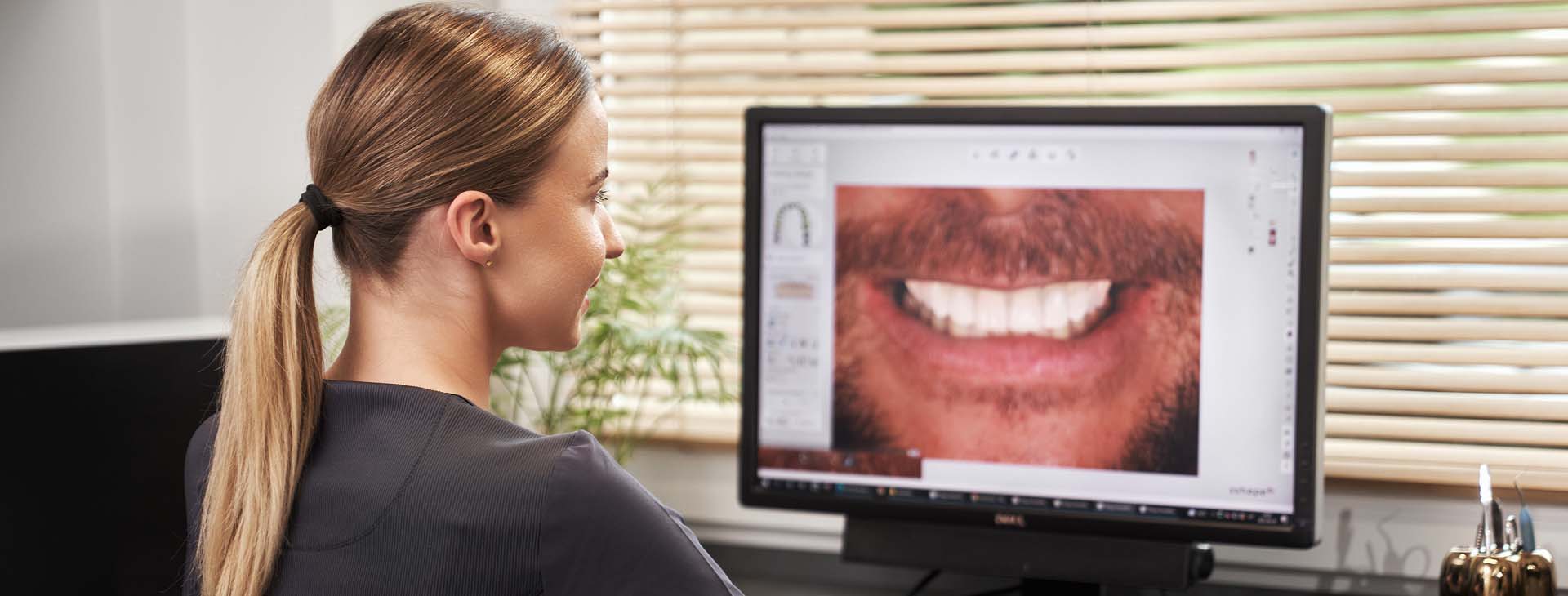

Digital smile design
It is great that today dentistry can use digital technology and visualization to provide an approximate image of the planned result.
When planning dental treatment involving restorative procedures (fillings, prosthetics), patients have a hard time imagining how they would look after the treatment, as changes involve the whole face, not only the smile. It is great that today dentistry can use digital technology and visualization to provide an approximate image of the planned result.
The smile and the face are very aesthetically important, and their parameters are defined by many lines, curves, formulae and proportions. In dentistry, just like in design or architecture, before beginning the project, a 3D design is produced, to predict the final result before work has even begun.
In dentistry it is called digital smile design. How is it done? Everything begins with standard photos of the patient’s smile and face performed according to strict requirements. In more challenging cases, facial scanning is done. Afterwards the patient’s tooth shade and shape selection is performed to predict the tooth appearance after restorative procedures.
Digital smile design and implementation can be performed in several stages:
- 2D smile design;
- 3D smile design;
- Mock-up restorations;
- Provisional restorations;
- Definitive restorations.
2D digital smile design
In order to perform digital smile design properly, the doctor must thoroughly evaluate the patient’s condition, perform X-ray and clinical tests. Then, the plan is presented for the patient, who sees the planned results and changes to their smile on the screen. During this visit we can discuss possible changes, communicate clearly and avoid any misunderstandings during the treatment; without visualization it is very difficult to judge, whether the clinician’s and the patient’s view on what is an attractive smile is similar.
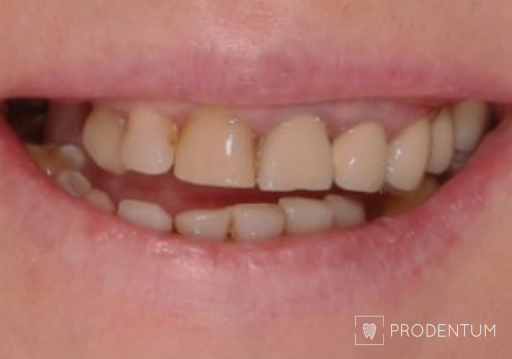
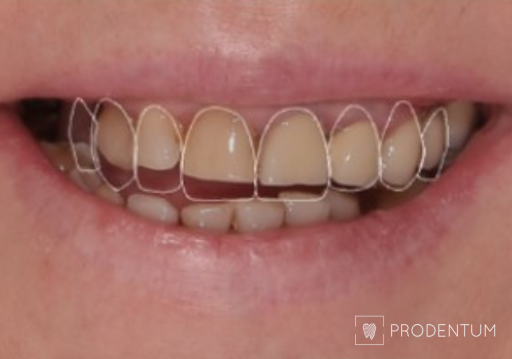
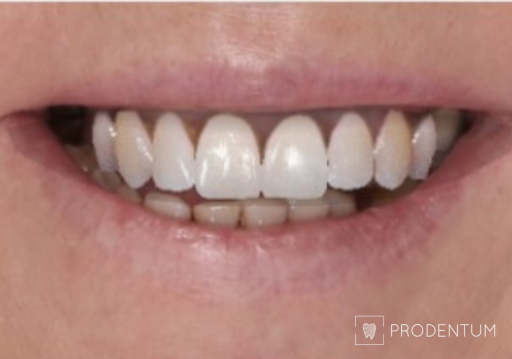
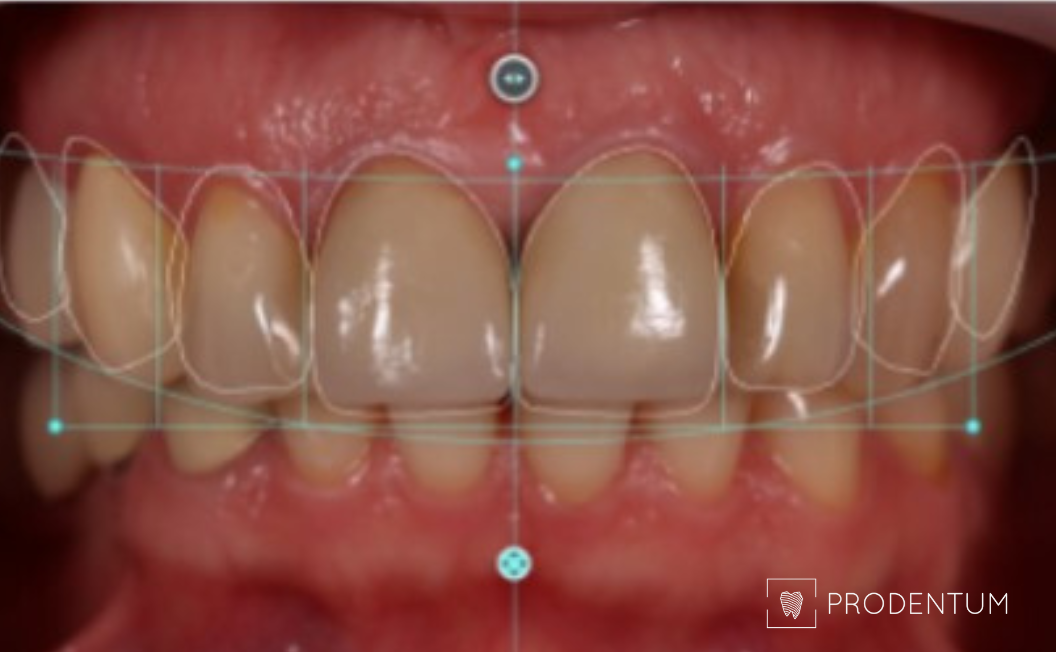
2D digital smile design. A. Initial situation. B. Planned restoration form according to aesthetic recommendations. C. Simulation of the shape and shade of the final restorations.
3D digital smile design
The possibilities of 2D digital smile design are limited, so in other treatment phases we recommend 3D digital smile design. The data from the planned digital smile design can be used for restorations using CAD (computer-assisted design) software. During this design phase, more aspects are evaluated: how the tooth shape will change, how that will affect the bite (it is simulated using special software), how lower jaw movement will happen, etc. During this phase the patient can once again evaluate, this time in a spatial environment, the planned tooth shape, see how the face will look like with the planned smile, and, if needed, ask to change the planned tooth shape or other aspects of the smile.
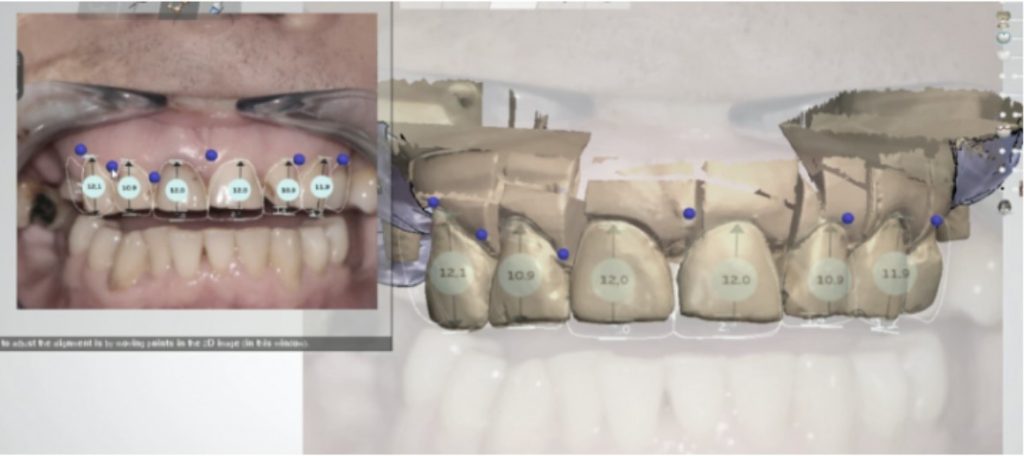
Mock-up restorations
Mock-up restorations are a way to try out the planned smile. Using this method the patient can evaluate in the real world how their smile will look and feel after the treatment. Along with the changes to appearance, other aspect are evaluated, such as the bite, pronunciation, etc. This process is done using mock-up restorations, i.e., recreating the planned smile using a temporary resin and a special matrix. This technique is a unique possibility to see the new smile for yourself and even to show it to your significant other. The patient can even present an example of the smile they way, be that a relative, a friend or even a Hollywood star! If parameters of the face and smile allow, we transfer the smile into the digital smile design of the patient.
In the traditional method, the mock-up restorations are models on a stone model of the patient’s teeth. Even though this is still used, it is inconvenient, takes a lot of time, and recreating the 3D-modeled shape by hand is very difficult. An alternative is 3D printing the new shape of the teeth. Silicone guides are made on the 3D-printed model, and is used to transfer the new smile design on the patient’s teeth so that they can experience the new smile, check whether they have any difficulty with certain sounds, and evaluate other aspect of the smile.
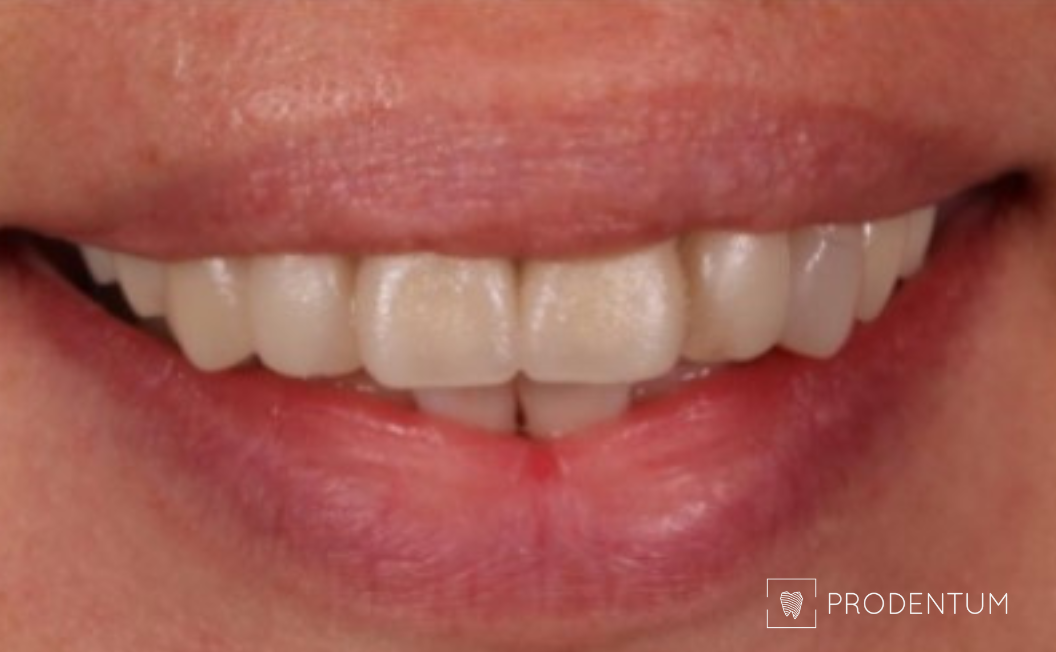
Mock-up restorations were prepared using methods of digital 2D and 3D digital smile design. The patient can evaluate the planned smile.
Provisional restorations
After we agree on a smile design, using CAD/CAM technology, we can produce provisional restorations (e.g., crowns). They are made from a very resilient aesthetic resin, and CAD/CAM technology allows us to manufacture them in a short amount of time. This method is especially useful for patients from abroad, who plan to stay in Lithuania for only a short while. These provisional crowns are very aesthetically pleasing, and they have a very low probability of fracture. This method is most commonly used when the anterior teeth need to be extracted, and dental implants are necessary. The patient can evaluate the bite and changes in appearance. If needed, small corrections can be done to the provisional restorations.
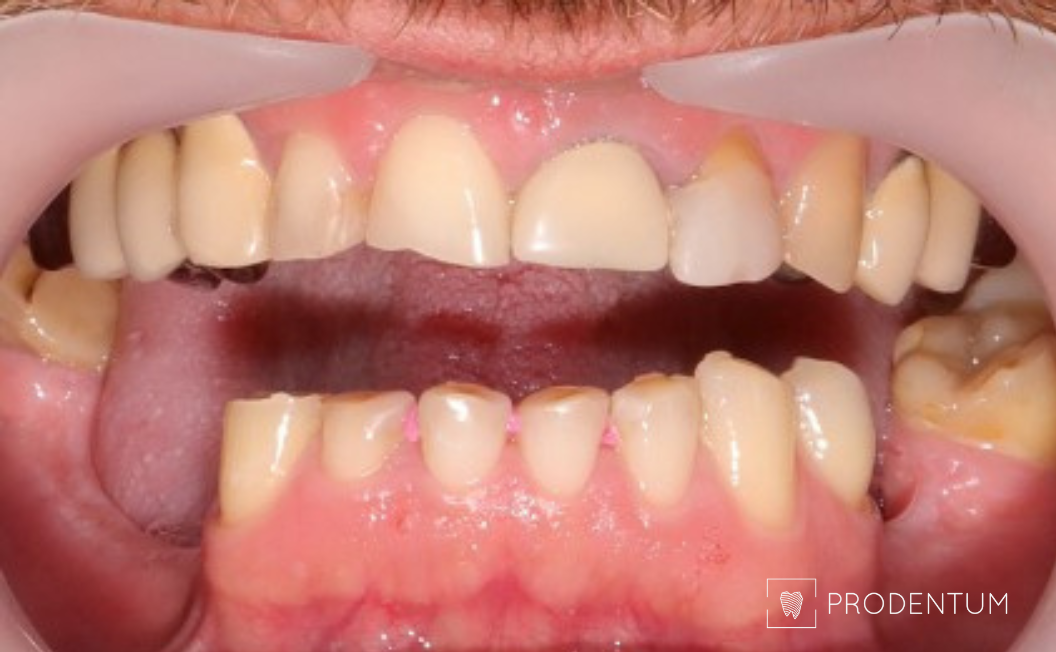
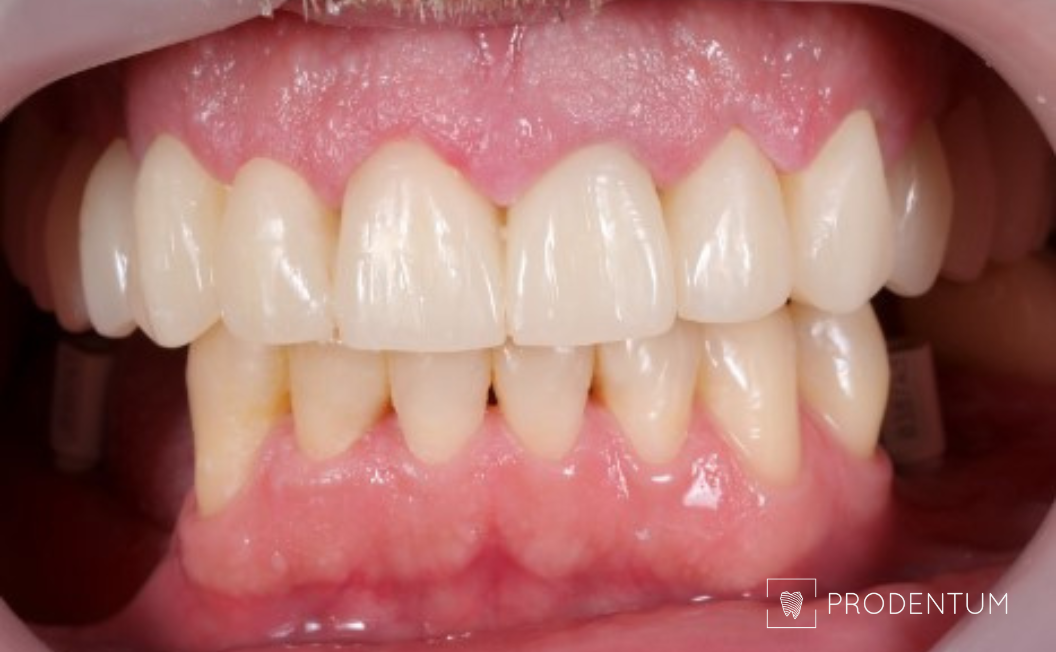
Provisional prosthesis made using digital smile design to restore chewing function and aesthetics.
Definitive restorations
Definitive restorations are cosmetic bonding, ceramic veneers, also onlays, crowns, bridges, etc.
The main requirements for the definitive restorations are aesthetics, resilience and impeccable accuracy. We achieve these results using digital technology – intraoral scanners, which are used to make a digital model of the patient’s teeth. Usually these scanners are used for smaller scale cases. However, TFW (Accurate digital implantology and prosthodontics) protocol, created in ProDentum clinic, allows us to employ digital technology more effectively even in large-scale tooth arch defects. Modern technological solutions expedite the process and reduce patient discomfort.
Definitive restorations are manufactured using the digital 3D shape of the provisional restorations. Using special software, definitive restorations are modeled and later on manufactured from the materials specified by the dentist. The final stage of manufacturing is done using digital milling machines to reduce the risk of discrepancies and control the accuracy of the definitive restoration.
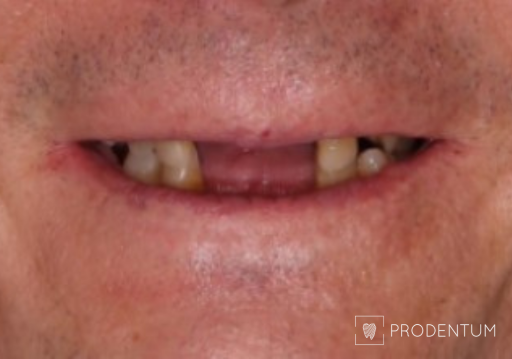
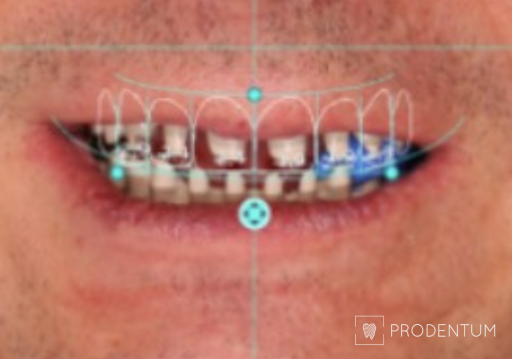
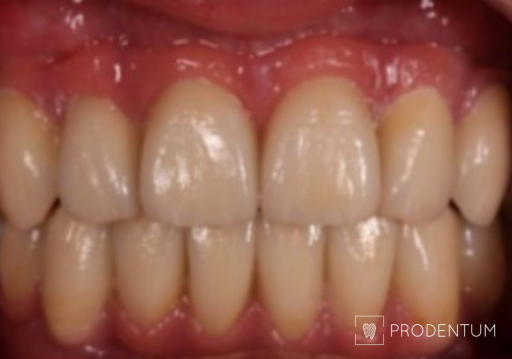
A thorough examination revealed that all remaining teeth are to be extracted. Digital smile design ensured that the initial planned shape is transferred to definitive implant-supported prosthesis.
After considering patient’s requests, tooth condition, anatomy, mechanical and optical properties, the clinician chooses the most appropriate restorative material. For accurate color reproduction, spectrophotometry and digital photography is used. Aesthetic restorations are usually made from ceramic.
Other recommended treatments
The ProDentum clinic has a wide range of services and provides patients with the highest level of professionalism.




